4 mins read
Seeking A Competitive Data Analytics Edge With Edge Computing

April 26, 2024
Copyright 2023, IT Voice Media Pvt. Ltd.
All Rights Reserved

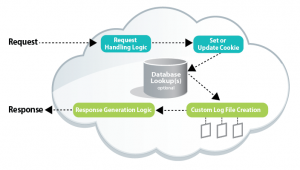 private and public sector, data stores based around databases and ancillary applications has increased exponentially. In the current Web-based and digital era, even more data hoards and data stores are being created. It’s a given that much of data stored, hoarded or archived loses its value over time. Analysis is the key to keep data useful and relevant for all business-related processes and operations and core organizational activities.
private and public sector, data stores based around databases and ancillary applications has increased exponentially. In the current Web-based and digital era, even more data hoards and data stores are being created. It’s a given that much of data stored, hoarded or archived loses its value over time. Analysis is the key to keep data useful and relevant for all business-related processes and operations and core organizational activities.